To attain the ultimate figure, you know that lifting weights should be in your game plan—so, you join a gym.
The issue is—most women have no idea what they’re doing.
The plethora of equipment, together with confusing nutritional advice, is overwhelming. So, you accept that unless you quickly gain a grasp on this new world—you’d only stick to the cardio-heavy habits.
In this guide, you will find the answer.
Consider this Women Weight Training Program the bible of female muscle growth.
- Table of Contents
Women and the Bodybuilding Myth
Not enough women lift weights—and that’s a shame.
Many women are concerned that hitting the iron will turn them into masculinized hulks—taking away their femininity and leaving them looking bulky and, quite frankly, scary.
Let me dispel this fallacy straight away—that will not happen.
Women cannot pile on muscle at the same rate as male counterparts—it’s physiologically impossible. The reason guys become so big is because of testosterone—the male hormone.
Testosterone is highly anabolic—it promotes massive muscle growth. Girls have relatively low amounts of this hormone in their bodies—on average men have around 675 ng/dl of testosterone, women just 30 ng/dl.
I know what you’re thinking.
You’ve seen photos and videos of heavily muscle-bound and tanned female bodybuilders—only distinct from the guys because they’re wearing a bikini.
Women can achieve enormous bulk—but they’ve been dosing up on illegal steroids—vastly increasing their testosterone levels. If this is the route you want to go down—good luck.
Just remember it will lead to facial hair growth, an enlarged clitoris, heart issues, and a deeper voice.
So, if you’re not going to build immense muscle mass—what’s the point of following a female weight training program?
I’ll tell you.
Why Women Should Lift Weights
Resistance training will not lead to massive bulk—but it will build muscle.
While typical cardio exercise can lead to weight loss—it does little for tone and definition. By encouraging a caloric deficit—where expenditure exceeds intake—fat is lost.
However, extended aerobic sessions can lead to loss of definition.
Your body will only utilize a certain amount of fat for energy—it still keeps some in reserve for survival. When these reserves have hit their minimum—the body begins to use muscle and protein for energy.
Hence you’re losing weight—but dropping muscle mass and sagging in all the wrong areas.
Following a bespoke women’s weight training program leads to the ultimate beach-ready figure.
By building muscle throughout the body—you appear tight, toned, and defined.
Furthermore, it elevates your femininity and curves. Exercising the chest raises the breasts, making them appear larger—working on the glutes and quads emphasizes your hips and produces a jaw-dropping booty.
In brief, female weight training will:
- Drop fat—research shows that resistance training burns fat during exercise and throughout the following 48 hours.
- Improve sleep—imperfect slumber is associated with weight gain.
- Elevate cardiovascular health.
- Heighten bone strength—essential, as women are more likely to suffer from osteoporosis than men.
- Make you look phenomenal—boosting your self-confidence.
How to Complete Your Weight Training Program Workouts: The Basics

This female weight training program requires you to concentrate on two areas—exercise and nutrition. These are equally as important and work synergistically to promote the perfect physique.
The remainder of this program concentrates on these vital parts of your body-enhancing regime.
Notice the title of this section—it’s a program.
And that’s important.
You can’t merely wander between the nice-looking machines, do as many reps (repetitions) as you feel like, and enjoy extended breaks between sets taking selfies for your Instagram account.
Building the perfect body is akin to cooking. All the ingredients need to be combined in the right quantities, order, and for a specific amount of time (or in this case, reps).
As the weeks progress, your weight loading increases while the number of reps decreases. This leads to optimum muscle building results and elevates strength progressively.
Before we get down to the workouts themselves—here are some essential guidelines and tips.
Repetitions
Or Reps. These are the number of repetitions (for, say, curls, presses, squats) of a particular exercise you complete in one set.
Each individual exercise indicates the rep count. The weight loading is down to your own current ability. You should use a load that induces complete fatigue (that is, you can’t lift anymore) at the rep number stated.
Hence, if an exercise details eight repetitions and you finish all of these with energy to spare, your weight loading is too light.
You’ll see that in the program below, the number of reps decreases as the weeks pass. Therefore, the weights you are lifting will increase during this time—always exercising to the point of fatigue.
Sets
A set is the number of times you complete the reps indicated.
After each individual set, rest for between 90-120 seconds—then start on the next. After you’ve completed all the sets—take a break for three minutes and then begin the next exercise.
This allows ATP (adenosine triphosphate) levels to be replenished—enabling you to carry on with your workout.
The ideal female weight training program isn’t about extended two hour-long workout sessions. Usually, you will be in and out of the gym within the hour.
Cardio
Research indicates that the most effective female weight training program combines weight-work with some cardio. As such, I’ve included some aerobic activity in each of your daily workouts.
Each weight training day includes twenty minutes of HIIT (high-intensity interval training). These sessions should be challenging but not completely impossible.
Try to aim for 30 seconds of extreme work—followed by one minute of recovery—and repeat, until 20 minutes have elapsed.
One day per week includes purely cardio—no weights. This workout lasts around 45 minutes of continuous training—no breaks—at low intensity.
The benefits of combining cardio in your workouts include:
- Lowering your bad (LDL) cholesterol.
- Reducing the chance of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Lowering blood pressure.
- Helping to maintain a healthy blood sugar balance.
- Assisting with weight loss
- Strengthening the immune system by increasing immunoglobulins.
- Elevating focus and cognitive performance.
- Enhancing mood and reducing the symptoms of depression.
Warm-Up
It’s essential that you warm-up before each training session. This reduces the chance of injury and allows you to perform to your maximum ability.
Ideally, complete a couple of warm-up sets before working a specific muscle group—by replicating the action of the particular exercise.
For example, before performing fully-weighted deadlifts—perform one set using just the bar (no weights), then a second set with half your usual workout weight. Then progressively overload the muscle with more weights for the working sets.
Hydration
When following this women’s weight training program, remember the words of the English poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge—water, water everywhere.
You should never underestimate the importance of remaining hydrated. Not only is it essential for health—but it also elevates performance and stamina.
Drink water before you exercise, after every 1-3 sets , and once you’ve finished the entire workout. Furthermore, continue to top up your fluid reserves post-training—whether you’re at home or work.
The Ultimate 12-Week Female Weight Training Program
Men and women can follow the same weight training program—with similar results.
However, specifically targeted exercises can help to accentuate the female figure. Hence I’ve developed a workout that enhances the natural curves of the female physique.
Fundamentals
This program places heavy emphasis on:
Squats
For tight and toned legs—together with an awesome butt—squats are the ultimate exercise. Combined with a barbell, they push the glutes, quads, and hamstrings hard—developing a killer physique.
Deadlifts
These compound exercises are ideal for all-around body enhancement—working the majority of the major muscles, including back (especially the lower back), legs, core, and obliques.
Lunges
Like squats, lunges are exceptional butt and leg boosters. What’s more, they improve flexibility and increase balance.
Pull-Ups
While a potent exercise for the biceps—pull-ups also work the back muscles—an area that’s often forgotten about among women trainees. You may look fantastic in your bikini from the front—but if you have a flabby and saggy back—you’re selling yourself short.
These exercises can be tough—especially for the weight training newbie. Luckily,
most gyms include an assisted pull-up machine—allowing you to complete the move easier.
Dips
This exercise is a great upper-body developer—working the chest, triceps, and shoulders.

Ideally, try to follow this workout as closely as possible for the best results. That being said—some adaptation will always be necessary.
The availability of machines, illness, and injury may lead you to make some small adjustments to the program—don’t worry about this. Just keep as tight to the regime as you can.
One final point.
These workouts are detailed by day—allowing Saturday, and Sunday as rest days. Naturally, work or family commitments may interfere and not allow training on specific days.
Alter the schedule as you wish, but adhere to these two points:
- Always allow yourself two days break from training per week.
- Never work the same area of the body on consecutive days.
12-Week Training Program
Monday: Lower Body
Exercise
week 1-4
week 5-8
Week 9-12
sets
reps
sets
reps
sets
reps
Leg Extension
3
15-12
3
10-8
3
8-6
Leg Curls
3
15-12
3
10-8
3
8-6
Stiff-Legged Barbell Deadlift
3
15-12
3
10-8
3
8-6
Barbell Squat
3
15-12
3
10-8
3
8-6
Standing Calf Raises
3
15-12
3
12-10
3
12-10
Exercise Ball Crunch (Abs)
3
15-12
3
12-10
3
12-10
Lying Leg Raise (Abs)
3
15-12
3
12-10
3
12-10
Conclude with high-intensity intervals on a treadmill for 20 minutes.
Tuesday: Upper Body
Exercise
week 1-4
week 5-8
Week 9-12
sets
reps
sets
reps
sets
reps
Dumbbell Side Lateral Raise
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Dumbbell rear delt raise
3
15-12
3
12-10
3
10
biceps Cable Curls
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Triceps Cable Pushdown
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Pull-Ups
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Dips
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Conclude with high-intensity intervals on an elliptical machine for 20 minutes.
Wednesday: Cardio
Exercise
week 1-4
week 5-8
Week 9-12
sets
reps
sets
reps
sets
reps
Low Intensity on Treadmill
1
30-45 mins
1
30-45 mins
1
30-45 mins
Thursday: Lower Body
Exercise
week 1-4
week 5-8
Week 9-12
sets
reps
sets
reps
sets
reps
Barbell Deadlift
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Seated Leg Press
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Dumbbell Lunges
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Hyper-extensions
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Seated Calf Raises
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Weighted Incline Crunch (Abs)
3
15-12
3
12-10
3
10
No HIIT or Cardio.
Friday: Upper Body
Exercise
week 1-4
week 5-8
Week 9-12
sets
reps
sets
reps
sets
reps
Barbell Bench Press
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Bent Over Barbell Row
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Dumbbell Shoulder Press
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
8-6
Biceps Barbell Curl
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Triceps Barbell skull crunsher
3
15-12
3
12-8
3
10-8
Conclude with high-intensity intervals on a treadmill for 20 minutes.
Rest Days
Resistance training is addictive.
It releases endorphins providing the ultimate high. This can mean that temptation arises, encouraging you to hit the gym even on your off days.
Don’t do this.
Remember earlier I stressed this is a natural female weight training program—and taking a break is part of that regime.
The old adage—too much of a good thing is bad for you—applies to bodybuilding.
Consider how muscle growth functions. Resistance training pushes muscles past their regular levels of exertion. This creates fiber damage, which the body then repairs and rebuilds.
Subsequently, this leads to muscle growth—allowing the body to cope with excess stress should it happen again.
However, if you overtrain muscles, this impinges on their repair—inhibiting regrowth.
Not only does pushing the body too hard lower the returns on the effort you’ve already expended—but it also messes with future training too.
If the muscles haven’t adequately recovered, they’re operating below par. Meaning fewer reps in your workouts—reducing the efficacy of your weight training program.
If the guilt becomes too much—go for a walk or do some very light jogging.
On your rest days—spend time with your family, friends, or pursue a hobby. Resistance training takes a lot of concentration—your brain needs to relax too.
Nutrition Plan for the Women Weight Training Program
I know what your thinking—oh no, diet time.
So many workout programs restrict your calories—leaving you tired, lethargic, and really lacking the motivation to hit the gym.
Weight training isn’t like that.
One of the most attractive features of building muscle is that you need to eat. It’s the fuel which drives creating chiseled tone and definition.
There are two areas of nutrition which need to be addressed in any weight training program for women—calories and macronutrients.
Calories
Generally speaking—for weight training, you need to increase your caloric intake. That is, to be in a caloric surplus.
These power packs of energy power you through your resistance training and are required to build muscle.
The simplest way to calculate your ideal calorie intake for muscle growth is to take your weight (in pounds) and multiply this figure by 20. Hence if you weigh 100 pounds, this means a calorie intake of 2000 per day.
For a more exact figure, which takes into account your activity levels and height, here’s a useful calculator.
Calculate your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE) or maintenance caloric intake, and increase that by 20 – 30% to ensure you are in a caloric surplus.
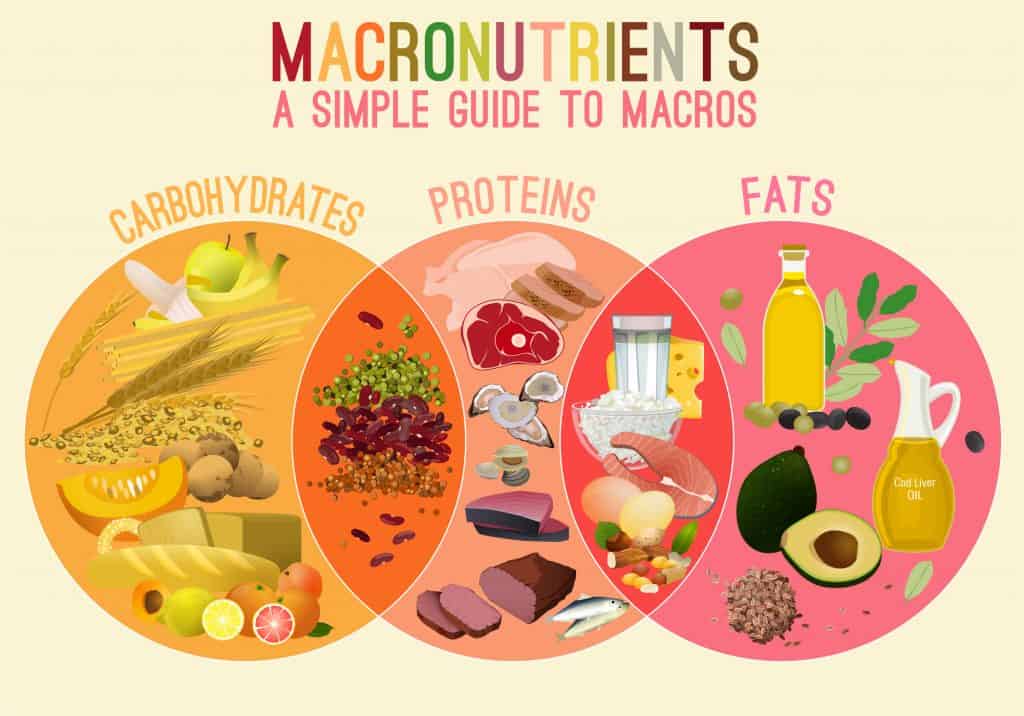
Macronutrients
While calories are important—you can’t eat whatever you want.
Muscle growth occurs when your macros (macronutrients) are at optimum levels—those being protein, carbohydrates, and fats.
Protein
Earlier in this guide, I explained that for muscles to grow, they need to repair. Protein, or more specifically the amino acids it contains, is the fuel behind this process.
The CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention) recommends that the normal daily requirement of protein is 0.36 grams per pound of bodyweight. However, for bodybuilding, this is insufficient and should be raised to 1-2 gram of protein per pound of bodyweight.
Good sources of protein include:
- Lean meat (i.e. chicken, red meat, fish).
- Eggs.
- Beans.
- Cottage Cheese.
- Greek yogurt.
Fats
Cut the fat to a minimum, right? That’s been the mantra of the fitness industry for the last 30 years.
Unfortunately, it’s terrible advice.
Fat is essential. It’s required for a healthy metabolism, provides energy, and also makes your food pleasurable to eat.
There’s only one fat to avoid—trans fats. These awful compounds, added by food manufacturers to promote shelf life and improve texture, are associated with heart disease and cancer.
For bodybuilding, the recommended dietary fat intake is around 15-30 percent of calories. That equates to approximately 0.3 grams for every pound of bodyweight.
Good sources of fat include:
- Butter (definitely not margarine—made from trans fats).
- Olive oil.
- Coconut oil.
- Avocados.
- Fatty fish like Salmon.
Carbohydrates
Keto, Low-Cal, and Atkins—it seems every dietician wants us to drop the carbs.
It’s another misnomer.
Not only are carbs typically packed with vitamins and fiber but also they’re the body’s “go-to” energy source. They power you through your workouts. Too little of this macro and the body will look elsewhere for fuel—including burning your hard-earned muscle.
That’s not to say all carbs are ideal. Concentrate on complex carbs, not the simple form. These provide more sustained energy levels, take longer to digest, stave off hunger, and don’t raise blood sugar levels as fast as the simple variety.
Total carb intake should represent your overall daily requirement, less protein, and fat needs.
Good sources of complex carbs include:
- Oats.
- Rice.
- Potatoes.
- Bananas.
Generally, I would recommend the following macro split:
- 40% Protein
- 40% Carbohydrates
- 20% Fats.
Here is a handy calculator that tells you how much that translates into grams for each macro in a given day based on your caloric intake.
Example of One-Day Muscle Growth Meal Plan
I’ve formulated an example meal plan to be used together with the weight training program above.
It’s designed to include the optimum levels of carbs, fats, and proteins to ensure muscle growth—based on the requirements of a 110-pound female bodybuilder.
Use this as a starting point to develop your own seven-day plan based on your personal preferences. I find the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) food database indispensable—use it to check the nutritional value of your foods.
Meal
Food
Macros
KCals
Meal 1
1 cup oatmeal
1 cup egg whites
1 tbsp Peanut butter
50 g blueberries
38.8 g carbs
36.3 g protein
11.7 g fats
405.7
Meal 2
5 oz chicken breast
1/2 cup rice
50 g broccoli
38.5 g carbs
46.5 g protein
10.4 g fats
432.6
Meal 3
5 oz chicken breast
1 baked potato (350 g)
50 g broccoli
40 g carbs
46.5 g protein
10.4 g fats
432.6
Meal 4
1 fillet Tilapia fish
1/2 cup rice
Veggies
41 g carbs
45.5 g protein
4.2 g fats
392
Meal 5
1 cup greek yogurt
1 oz mixed nuts
1/2 grape fruit
25 g carbs
24 protein
16 g fats
339.1
Total
200 g carbs
200 g protein
44 g fats
2000
Initially, it may appear to be an inconvenience to calculate your calorie and macro intake. However, after the first couple of weeks, it will become second nature—as you begin to understand the nutritional values of your preferred foods.
Remember—it’s crucial you concentrate on your dietary intake for the best results.
Supplementation for the Women Weight Training Program

Special dietary requirements, allergies, intolerances, and personal preferences can make obtaining sufficient nutrition purely from your food intake difficult.
There are many supplements for women available that not only make hitting your targets easier—but can also accelerate the returns from your weight training program.
Below are my favorite bodybuilding products for women—designed to boost results.
Whey Protein
Possibly the most crucial supplement in any weight training program.
Amino acids, the compounds which make up protein, are required for muscle growth. Nine of these, known as the essential amino acids, cannot be created by the body. You need to ingest them.
Whey protein, supplied in powder form and mixed into a drink or shake, includes all of the essential amino acids. While food intake can provide a certain amount—reaching the quantity required for optimum muscle growth can be inconvenient and expensive. Whey protein comes in different types including grass-fed, the highest quality, and organic.
These supplements make hitting your requirements easy. Furthermore, research shows that ingesting protein elevates the rate of fat loss.
Creatine
In the weight training program workout above—sets are completed to the point of fatigue. That is, however much you want to push out an extra rep, your muscles refuse.
The ATP in your muscles powers their contraction—every rep uses a little more. Since your body doesn’t contain unlimited resources of this chemical—fatigue rears its head, meaning the end of your set.
Creatine, probably the most essential supplement for athletes, restores your ATP—enabling you to workout longer and push the muscles harder—delivering faster results.
Pre-Workouts
Despite your enthusiasm and best intentions—on some days, your weight training will not be at optimum levels.
The stresses of work, finances, and family can drain you—leaving your workouts lackluster and your focus lagging.
Pre-workout supplements are a formulation of natural ingredients designed to elevate power, energy, concentration, and stamina. Consumed around 30 minutes before the beginning of your session—these products can elevate your performance and returns. Pre-workout supplements also come without stimulant substances.
Multivitamins
While creatine and whey have become gym-essentials for many female lifters—multivitamins are often neglected.
This is unfortunate. These products provide immense benefits to any female weight training program. They supply the body with nutrients and minerals to deliver the perfect conditions for muscle growth.
When lifting weights, we are placing heavy demands on our bodies. Often, our dietary vitamin intake is insufficient to meet these needs. Multivitamins address this issue.
The best weight training program multivitamins should include:
- Vitamin C—required for muscle collagen production.
- B vitamins—boosts muscle cell regeneration.
- Folic acid—essential for red blood cell creation.
- Iron—many women suffer from iron deficiency—a mineral required for muscle growth and stamina.
Beta-Alanine
If you find yourself struggling to hit your target reps—this amino acid, which occurs naturally in fish and poultry—prevents muscle fatigue during training.
While completing your weight training program—intense workouts can leave the muscles starved of oxygen. This elevates lactic acid levels—resulting in acidosis. You’ll recognize this as the unmistakable pain felt in the muscles during those final few reps.
Supplementing with beta-alanine encourages the body to produce carnosine—a compound that inhibits the build-up of lactic acid.
Hence, this reduces your pain and discomfort, and your endurance and stamina elevate The harder and longer you can push yourself—the faster results will appear.
Final Remarks
For the ultimate female physique—you need to lift weights and eat right.
But, going to the gym doesn’t have to be imposing. Consider the above guide to be your muscle-gaining ‘bible’—a complete weight training program for women.
By following the tips, workouts, and nutritional advice, you’ll witness remarkable improvements to your physique over a 12-week period.
And, for the ultimate in training returns, consider supplementation to seriously escalate results.
Stick to the above plan—and you will both look and feel amazing.