As someone who’s always been very fitness-focused, nutrition plays a vital role in achieving my goals.
Up until a few months ago, my diet was very carb-and-protein-centric—I thought it was the most effective way, and honestly the only way, to attain a defined and ripped physique in the cutting phase.
I was mistaken.
The keto diet has helped me burn fat more effectively—accentuating my muscles, but with caveats!
This article has everything you need to know about keto diet for bodybuilders.
- Table of Contents
What Is the Keto Diet?
The ketogenic diet focuses on a very low-carb, high-fat dietary regime that aims to promote weight loss.
Our bodies’ prime source of energy is glucose (carbs). By substantially reducing this food group, your body relies on alternative sources for fuel—body fat. It, however, differs from the paleo diet.
It’s similar to the Atkins diet in that it’s low-carb, high-fat—one of the main differences being the keto diet encourages more healthy fats.
You might wonder how it’s possible to lose weight on a diet consisting mainly of this macronutrient. In simple terms—following the keto diet shifts your body’s preferred fuel source to fat—boosting your body’s ability to burn fat.
How Does Keto Work?
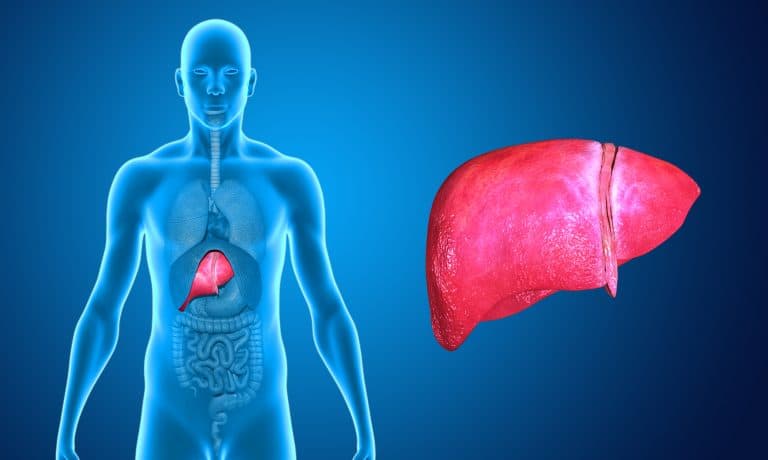
Your liver produces ketones from the fats you consume—by restricting carbs and increasing fats, these ketones become the prime source of energy for your body. This is a metabolic process called ketosis.
Due to a higher level of ketones in your body, a blood or urine sample will be able to tell you whether you’ve reached this metabolic state.
There are also some natural signs that your body will manifest:
- Weight loss.
- Bad breath.
- Thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Decreased appetite.
The keto diet was designed almost a century ago for patients with epilepsy. Research indicates that it induces positive results for the condition—the frequency of seizures dropped.
An alternative way to enter ketosis is by fasting. Followers of keto often apply this method in the bid to kick start the process.
However, studies suggest the timescales of reaching ketosis are comparable. Therefore, fasting doesn’t have to be compulsory.
The 5 Reasons When and Why Bodybuilders Should Follow the Keto Diet
Let me start with answering the question of when, first.
1
Fat Burning Efficiencies
A regular carb-based diet means your body has a constant, and all too often, an excess supply of fuel. Furthermore, with carbs on tap, your body doesn’t have to work for its energy supplies—quite literally, it’s handed over on a plate.
However, when following the keto diet, your body is denied this number #1 fuel source—and has to switch tactics.
Ketosis forces the body to become more resourceful and find another provider. It streamlines its energy processes, and as mentioned, utilizes stored fats for fuel.
This means you’ll be burning more fat, plus shedding the unwanted poundage will provide optimal body composition.
2
Muscle Protein Sparing Response
Gluconeogenesis—an alternative pathway the body takes to find non-carbohydrate sources to process into glucose (energy).
This includes protein, which as we know, forms the basis of muscle mass.
Following any form of a low-carb diet, the threat of musculature loss through gluconeogenesis is very high. As the keto diet is an extreme form of this regime, one would assume this principle would be exacerbated.
However, for a short period of time, say the last 6-8 weeks of the cutting phase, it’s the opposite.
Thanks to the high-fat diet and the ketones produced as a result of ketosis, your muscle is saved. These compounds inhibit muscle protein breakdown. The additional fat you are consuming is also another fuel source to divert the body’s attention away.
It is believed that providing protein intake is adequate, extreme low-carb diets like keto, are protective against muscle catabolism during short energy restriction.
I have to caution you, however, that if protein intake is low for an extended period of time, you might run into the risk of muscle catabolism due to extensive shortage of recovery building block, amino acids from protein. So, your muscle will not be able to recover from the breakdown caused by training.
3
Regulates Mass Building Hormones
Limiting your carbohydrate intake has an influence on blood sugar levels on the keto diet. Which, as a result, impacts on insulin.
This protein hormone plays an important role in muscle building—being a cofactor of muscle protein synthesis and prevents breakdown. It also has a close relationship with the anabolic growth hormone (GH).
Experts theorize that considering growth hormone production elevates during a low blood sugar scenario. The same principle could apply to the keto diet.
4
Appetite Suppression
Diet and hunger are often stereotypically associated with one another.
The keto diet is predominantly based around fats, yet protein intake is also a factor in your ratios. This macro is considered the most satiating.
Research also indicates the state of ketosis is another determinant in reducing appetite.
The Pros of the Keto Diet for Bodybuilders
Following the keto diet can provide additional advantages:
- Decreases frequency of epileptic seizures.
- Lowers cholesterol and blood pressure.
- May prevent type 2 diabetes.
- Regulates blood sugar levels.
- Improves skin conditions—acne.
- Alleviates symptoms of fatty liver disease.
- Anti-carcinogenic potential.
- Lessens occurrence of migraines.
Side Effects/cons of the Keto Diet
The keto diet is considered an effective and safe way to shed pounds and provide benefits to a number of health conditions.
However, transitioning into ketosis can cause temporary side effects—sometimes referred to as the keto flu—your body needs time to adjust.
The most common side effects include:
- Weakness/low energy.
- Headaches.
- Constipation.
- Diarrhea.
- Keto breath.
- Muscle cramps.
- Dehydration.
- Moodiness.
- You won’t get pump during workout.
- You won’t be able to build muscle.
What Can You Eat on the Keto Diet as a Bodybuilder?

Standard Keto:
Calorie ratios:
- Fat: 70%.
- Protein: 20%.
- Carbohydrates: 10%.
High-Protein Keto:
Ideal for bodybuilders a short cutting phase who want to follow a low-carb, high-fat diet and preserve their muscle mass.
Calorie ratios:
- Fat: 65%.
- Protein: 30%.
- Carbohydrates: 5%.
Modified Keto:
This plan is less restrictive. It can be helpful if you’re starting the keto diet—transitioning gradually into a low-carb meal plan.
Calorie ratios:
- Fat: 40%.
- Protein: 30%.
- Carbohydrates: 30%.
Cyclical Keto:
This variation bases its principles on the standard keto diet, but it allows you to eat carbs on certain days of the week. Bodybuilders favor this method to gain mass.
You choose a day for carb-loading—to replenish glycogen stores—in readiness for a mammoth training session.
For example, you plan a carb feed, then hit the heavy plates the following day. The theory being you can workout at peak performance levels. Plus, you need to put in maximum effort to deplete any stored carbs from your body.
Targeted Keto:
This plan follows the standard keto diet but includes eating carbs pre-workout. It’s believed, exercise will trigger the body to use the recently ingested carbohydrates immediately for fuel.
Keto and Net Carbs
Unlike most other diets, the keto diet focuses on net carbs. That is, the remaining number of carbs after subtracting the fiber content.
The basic equation:
Total Carbs – Fiber Content = Net Carbs*.
Your total daily figure must reduce to 20-50 grams per day to reach a physiological state of ketosis.
* There is contradictory evidence regarding calories in fibers. While the FDA estimates fibers to have 1.5 calories per 1 gram of fiber (as opposed to 4 calories per 1 gram of carbohydrates), other institutions have a different definition of fibers let alone calories contained in them. Regardless, calories in fibers are small enough to be neglected.
Should You Count Calories on Keto Diet?
Many advocates of the diet claim that counting calories aren’t necessary.
However, this is the most catastrophic mistake you can make. Consume more than your caloric goals, even on the keto diet, and you will gain fats like that! (you can imagine me snapping my fingers, right?!). Consume less, and you will lose energy, strength, stamina and, certainly, muscles.
The number of calories you consume in a day will depend on your height, age, gender, current weight, and fitness goals.
As the first step, use the below body weight planner to estimate how many calories you will need.
For the second step, once you know what your maintenance caloreis (TDEE), reduce that number by 20-30%. That should be your target calories to lose fats.
Use the following calculator to set your target weight goal for 6 – 8 week keto diet period, and it should tell you your target weight after that period.
Finally, use the macronutrient calculator below and set the macro targets to one of the keto variations above (say standard: 70% fats, 30% protein, and 10% carbs). The calculator then will translate that figure you obtained from the BMR and TDEE calculator to daily grams of carbs, fats, and protein.
Fats have more than twice the number (9 cals) than carbs per gram (4 cals). This means your portions per calorie will be smaller on the keto diet.
Recommended List of Keto diet Food
A keto diet consists of foods that are high in fat, moderate in protein, and—most notably—low in carbs.
Here is a summary of the foods you need to stock up on:

Green leafy vegetables:
are nutrient-dense and low in carbs.

Grass-fed meats and poultry:
protein-rich and zero carbs, they’re a vital source on the keto diet. Grass-fed is always a better option.

Oily fish:
such as tuna and salmon are low in carbs and rich in essential fatty acids.

Eggs:
are low-carb, high in protein and fats. They also contain vitamins D, E, A, and B complex, plus minerals—calcium, zinc, and selenium.

Nuts and seeds:
rich in healthy fats, this is an ideal option for vegans and vegetarians on keto. Avoid any products with a form of coating—keep it natural.

Full-fat dairy products:
including full-cream milk, cheese, and butter. They’re a great source of fats and essential minerals.

Low-carb fruits:
many fruits are loaded with fructose, so make sure to eat fruits with a lower sugar level—such as berries, avocados, and watermelon.

Low-carb vegetables:
stock up non-root/non-starchy kinds—cauliflower, cabbage, asparagus, artichokes, mushrooms, peppers, tomatoes, and zucchini.

Healthy cooking oils:
extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, and sesame oil.
Foods To Avoid
Foods that contain high levels of sugars and starch should not be consumed on a keto diet.
These include:
- Pasta.
- Bread.
- Oatmeal.
- Rice.
- High-carb fruits (bananas, mango, pineapple, apples).
- Dried fruit.
- Carb-laden vegetables (sweet potato, pumpkin, beetroot, carrots, onions).
- Pastries.
- Candy.
- Soda and juice.
- Processed and fast foods.
A Keto Meal Plan For Bodybuilders
You’ll find below a simple three-day meal plan based on the above that you can use as an example for the keto diet.
Day 1:
Meal 1
Mushroom omelet.
Meal 2
Chicken-caesar salad with ranch dressing.
Meal 3
Pork chops with grilled asparagus.
Meal 4
Full-fat yogurt with mixed berries.
Day 2:
Meal 1
Eggs fried in butter with spinach.
Meal 2
Tuna salad with peppers and tomatoes.
Meal 3
Roast chicken and cauliflower with melted cheese.
Meal 4
Mixed nuts.
Day 3:
Meal 1
Blueberries and cream cheese on avocado halves.
Meal 2
Grilled salmon on a bed of spinach and tomato.
Meal 3
Steak with fried mushrooms and roasted zucchini.
Meal 4
Celery dipped in almond butter.
Tips for Training on A Keto Diet
When you commence the keto diet, your body needs time to adjust to the carb restriction. Some of its processes and systems will change as it begins to adapt.
What this means for your workouts:
- It will feel more challenging to execute sets of long durations—at first. Going beyond short timeframes will impact on your strength and endurance capacity.
- Lower the number of reps to a maximum of 12 – 10, double your usual rest period and keep it to a maximum of four sets.
- Lay off lifting too heavy at the beginning. Gradually increase the weights as you’re adjusting to ketosis.
- The muscles in your legs are stronger than the muscles in your upper body. Squats and lunges will be challenging to perform than exercises that work your upper body muscles.
- Avoid intense cardio sessions like HIIT or interval training. But make sure you incorporate a short 10-minute warm-up and cool-down into your workout.
- The targeted or cyclical keto diet might be a better option if you plan on doing longer lifting workouts—it will provide you with more fuel.
Once your body has become keto-adapted to its new energy source, you can resume your usual tempo—and reap the benefits that the keto diet will provide to your workouts.
Workout Plan Examples
I’ve devised a simple workout plan for you to use while adjusting to ketosis. Aim to complete the entire number of sets per exercise before moving on to the next.
Furthermore, try not to exercise on consecutive days—rest and recovery are equally important.
Day 1 (low intensity)
Exercise
sets
reps
Rest
Squat
4-5
10 - 6
3 - 5 mins
Leg Presses
4
10 - 8
3 - 5 mins
walking lunges
4
10 - 8
3 - 5 mins
Hamstrings curls
5
10
3 - 5 mins
Calf Raises
5
failure
2 - 3 mins
Day 2 (Mideum Intensity)
Exercise
sets
reps
Rest
Bench press
4
10 - 6
3 - 5 mins
Shoulder Press
4
10 - 6
3 - 5 mins
Bench Flyes
4
10 - 8
3 mins
Dips
3-4
10 - 8
3 mins
Shoulder lateral raises/rear raises*
3-4
12 - 8
3 mins
Tricep Presses
4
10 - 8
3 mins
Tricep skull crusher
4
10- 6
3 mins
* superset
Day 3 (high intensity)
Exercise
sets
reps
Rest
Deadlift
4
10 - 6
3 - 5 mins
Barbell Row
4
10 - 6
3 -5 mins
pull-ups
4
12 - 8
3 - 5 mins
Bicep dumbbell curls
4
12 - 8
3 mins
Bicep Preacher Curls
4
10 - 8
3 mins
The Best Supplements for Keto Diet
The supplement market for ketogenic diet has exploded. From keto meal replacements to keto bars, stick to high quality brands. Here is a list of recommended keto supplements:
1
MCT Oil
A supplement made up of medium-chain triglycerides—a type of fat contained in certain fatty foods such as dairy products and oils. It’s mostly used as a weight-loss remedy or performance enhancer.
These fats travel straight from your gut to your liver, where they are turned into ketones directly. This means they’re less likely to be stored in your body’s fat reserves, as they’re being used immediately.
MCT oil also comes with health benefits:
- Increase in brain function.
- Enhances exercise endurance.
- Weight loss.
As it’s calorie-dense—taking these supplements while you’re not in ketosis can result in weight gain.
2
Exogenous Ketones
Exogenous Ketones is the go-to supplement for when you’ve indulged in a non-keto meal. It contains ketone beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)—an organic compound your body produces naturally.
Consuming exogenous BHB raises the number of ketone bodies in your blood—speeding up the process of ketosis.
These supplements tend to contain ketones that are bound to sodium—this could pose health risks for people with high blood pressure.
3
Magnesium
A mineral that is essential for over 300 processes within the body—including regulating muscle function, blood pressure, and protein synthesis.
Many magnesium-rich foods are also high in carbohydrates. This can make it challenging to consume adequate levels of this mineral while on the keto diet.
A supplemental dose of up to 350 mg per day—can help reduce muscle weakness and cramps, fatigue, insomnia, and irritability.
4
Omega-3
Omega-3 is rich in the fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). EPA and DHA reduce inflammation and risk of heart disease.
Studies found that supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids on the keto diet decreased insulin, inflammation, and risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, it promotes a healthy omega-3 to omega-6 ratio—promoting energy levels and overall health.
5
Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine is one of the best performance boosters, with an outstanding safety record. It’s shown to increase muscle mass, strength, and exercise performance.
Several types of creatine supplements are available, but the monohydrate form is considered the most popular. After the loading phase continue with a maintenance dose of 5 grams daily.
6
HMB
Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) is a metabolite of the essential amino acid leucine.
When you dramatically lower your carb intake, you need to protect your muscles from being broken down (muscle loss). HMB triggers protein synthesis and has anticatabolic properties—preserving and promoting muscle mass without needing to increase protein intake.
HMB in doses of 3 grams per day is considered safe and may even reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Six Common Mistakes Bodybuilders do during a Keto Diet
Before we discuss the common mistakes, I have to stress once again that the most obvious mistake is not counting calories thinking you can eat whatever fat source you want without consequences. Another big mistake is thinking that you can build (or even preserve) muscle on a keto diet if you’re doing it for an extended period of time, as I discussed above.
With that being cleared out, here are other common mistakes while being on the keto diet.
1
The Fear of Eating Too Much Fat
We’ve been conditioned to believe that foods with high-fat content will make us fat.
For the keto diet to be effective, you need to let go of that mindset. When you deplete your body of carbs, it needs another source of fuel—if you don’t provide it, you’ll become lethargic.
Fat will be your friend. The fats you consume won’t be stored in your body for later use once you’ve reached ketosis. Instead, it’s converted to energy directly—because it’s the only sufficient energy source your body has.
Consume as many calories as your body requires, not above or below—keeping the calories from fat at around 70%.
2
Overdoing Protein Intake
Consuming higher amounts of protein than fat on the keto diet won’t make you enter ketosis—but gluconeogenesis. That is, when your body utilizes protein for fuel.
Once protein becomes the primary source, you’ll be eating too few carbs for your body to rely on glucose, but not enough fat to be ketosis. All of the fat you’re eating will be directed into fat stores—resulting in weight gain.
Aim for an absolute maximum of 30% of your calorie intake to come from protein per day. Meats, fish, and poultry are an essential part of the keto diet, but it shouldn’t account for the majority of daily caloric intake.
3
Low Sodium Intake
Insulin communicates with your kidneys to store sodium. A low-carb diet causes insulin levels to drop—so it’s not able to convey messages as effectively. As a result, your kidneys begin flushing out this mineral, which can lead to the “keto flu.”
Increase your sodium by adding salt to your meals—especially around the time of working out.
Your body is more susceptible to losing all the electrolytes when in ketosis, namely potassium, magnesium, phosphate, and calcium.
Eating plenty of dark, green leafy vegetables, and avocados will help you meet your potassium requirements. Chicken and turkey are particularly high in phosphate, and dairy foods are a good source of calcium.
Nuts are rich in magnesium. However, I recommend taking a magnesium supplement.
4
Not Drinking Enough Water
Hydration is a top priority regardless of the diet you’re following. But water intake, in particular, should be notably increased.
Water retention is a known trait of carb-laden diets. Therefore when restricting carbs—you lose water. For most people following the keto diet, any initial weight decrease is typically due to water weight.
This will dehydrate you.
Assess your hydration levels by the color of your urine—darker yellows mean you need to drink more water.
5
Underestimating Your Carb Consumption
It’s easy to become addicted to carbs when they’re so well hidden. Always check the nutrition label to see how many net carbs are in a product before you buy it.
Sugars can be listed as something else on the ingredient label. Watch out for the following terms:
- Fructose.
- Corn syrup.
- Sucrose.
- Dextrose.
- Lactose.
- Barley malt.
- Rice syrup.
- Agave.
- Maltose.
- Molasses.
- Malt syrup.
- Honey.
- Cane juice.
- Fruit juice.
Don’t buy a product unless you’re sure it’s low-carb.
6
Being Impatient
One of the main reasons people give up on the keto diet (or most diets for that matter), is because they don’t allow enough patience to see it through.
Switching to a completely different metabolic process after relying on glucose for your whole life isn’t going to happen in a day. And it won’t be particularly comfortable.
Don’t let the transition and adaptation process demotivate you. Once you’ve hit the sweet spot of ketosis, you’ll feel better than before.
The Takeaway
The keto diet has shown to provide many benefits to those who become keto-adapted—successfully.
When bodybuilders bulk up, unless they’re eating clean—body fat accumulates. The keto diet will help you shred that fat effectively in the cutting phase—resulting in significant musculature definition.
However, to reach your goals while following the keto diet—you need to stick with it for 6-8 weeks max. There’s little room for slip-ups—load up on too many carbs, and you’ll get knocked out of ketosis—focus on fats and, to a lesser extent, protein.
Follow this guide to the keto diet for bodybuilders to stay on track.