I was training six days a week and tracking my macros to the percentage, yet I still couldn’t get anywhere near my target.
I bumped into some fellow hardgainers at the gym—who shared some valuable advice with me. It made the difference, and in no time, I was powering through this hurdle.
Consider this your complete guide on how to transform your physique from skinny to muscular.
- Table of Contents
Why You Aren’t Gaining Weight
In short—consuming fewer calories than you use each day, means you won’t gain mass.
Various factors can affect how fast—and how many—calories your body burns—activity levels, genetics, and metabolic rate.
Being aware of what’s influencing your weight can help you determine how to change your diet and workouts according to your goals with muscle gain.
The Science Behind Being Skinny
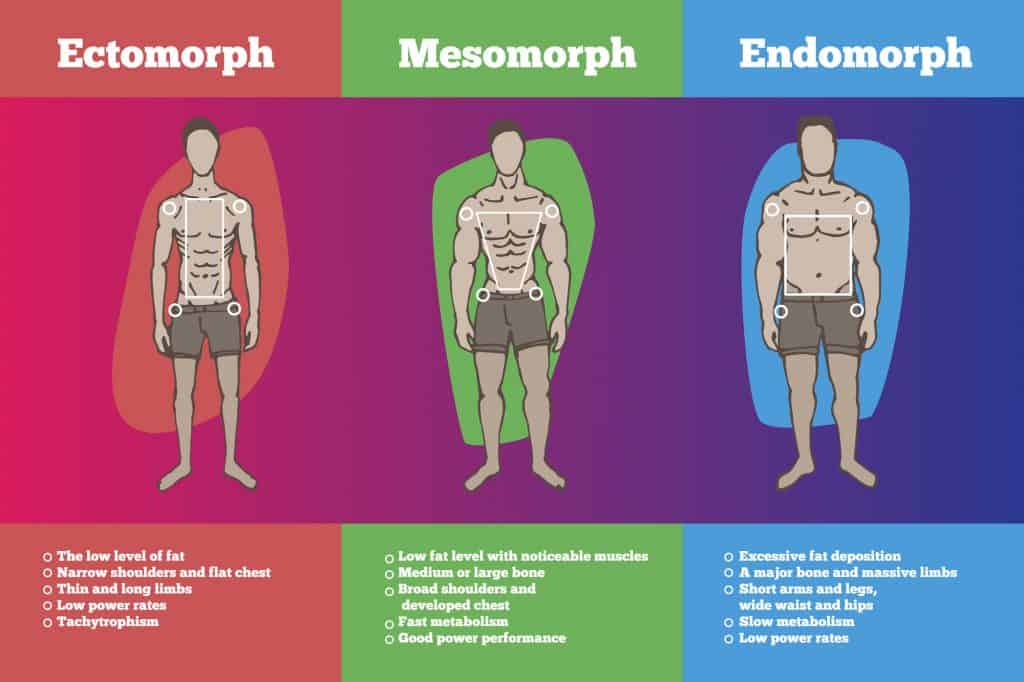
Genetics
Your biological make-up has an impact on the efficacy of your diet and workouts. The three different somatotypes (body types) are known as:
Mesomorph
People with naturally athletic physiques—large bone structure and muscles. Those with a mesomorph build, gain, and lose weight fast.
traits:
- Solid body frame.
- Well defined muscles.
- Rectangular shaped physique.
- Strong.
Endomorph
People who gain weight quickly. They usually have a shorter build with thick arms and legs. The endomorph body type is typically soft, but they can gain muscle with little effort.
traits:
- Round body.
- Lacks muscle definition.
- Slow metabolism.
- Struggle to lose body fat.
Ectomorph
Your typical skinny guy or girl. If you have an ectomorph body type, you have a faster metabolism and find it tough to gain weight.
traits:
- Thin.
- Flat chest.
- Small shoulders.
- Lean muscle mass.
- Low body fat.
High Metabolism
If your metabolic rate is high, it means your body burns calories more rapidly—leading to a skinny physique and difficulty gaining muscle.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Your BMR is the amount of energy (calories) your body needs to support homeostasis—the essential physiological functions for life. This accounts for 50-80% of your daily energy use.
To find out your BMR, use the following calculator.
Factors which can influence this biological rate include:
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Environmental—extreme temperatures cause your body to work harder to regulate core temperature—increasing your BMR.
- Infections—your body needs more energy as it works harder to recover.
- The thermic effect of food—defined as the increase of metabolic rate following ingestion of a meal. Macronutrients lift the metabolism by different ratios—protein:20-30%, carbs 5-10% and fats 0-3%.
- Drugs—stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine can increase your BMR.
7 Tips to Gain Weight Effectively

To gain muscle mass, you first need to assess your current weight. Take note of your metabolic rate (BMR)—and set a goal.
Take on board these essential tips to go from skinny to muscular:
1
Eat More
After you determine your BMR, the calculator above will also tell you your daily calories to maintain your current weights or (TDEE). This is the number we actually want because it is a function of your daily activity.
Once you figure out your TDEE, increase that by %20-%40. For example, if your TDEE is 2000 calories, you will need to consume 2400 – 2800 calories a day. In other words, you need to be in a caloric surplus.
It’s pretty simple—if you consume more calories than your body burns, you’ll gain weight.
Let your scales be your gauge—if you don’t see an increase when you step on them, reassess and up your intake.
2
Frequent Meals
Buck the three-meal-a-day trend and switch to five or six mini-meals. It’s a simple way to increase your intake, plus smaller portions will be lighter on the stomach.
3
Eat The Right Foods
Upping your intake doesn’t mean all foods are on the menu. Loading up on “empty calories” will make you gain fat, not muscle. It’s also not a reliable source of energy.
Focus on eating both caloric and nutrient-dense whole foods that are high in carbs and healthy fats—like pasta, beans, avocados, and nuts.
4
Drink Your Meals
If you’re increasing your calorie intake, a liquid lunch or snack is an alternative. Consuming foods in a fluid form is easier to digest than solids—it’s already broken down.
It cuts down digestion time, and you’re also less likely to experience that heavy feeling from a proper meal.
5
Eat More Protein
Eating protein-rich foods is essential for muscle growth.
Muscle damage occurs naturally during exercise—muscle protein breakdown (MPB)—the protein your muscles lose as a result of training.
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is the process your body deploys to counteract the above—producing protein to repair these damaged muscles.
To gain muscle, your MPS needs to exceed your MPB—and this won’t happen without an adequate amount of protein to fuel the sequence.
Make sure to eat healthy proteins such as lean meats, chicken, fish, eggs, or soy products like tofu if you choose the vegan route.
6
Strength Training
Resistance training is what you need to focus on—lifting weights builds muscle and body strength.
Cardio will shed body fat—which is great if you’re cutting. However, it’s not so great for gaining muscle—too much is considered catabolic. Don’t do it more than twice a week.
Keep the training balance tipped firmly towards lifting the heavy iron.
7
Consistency Is Key
Don’t expect to go from skinny to muscular if you’re not consistent. You’re skinny now because you’re consistently burning more calories than you’re consuming.
The same principle applies when trying to attain a muscular body.
Selectively increasing your calorie intake and the intensity of your workouts won’t produce results—it should become part of your daily routine.
Effective Nutrition Plan for Skinny Guys

You’re aiming to become muscular, and as mentioned—to achieve that, you need to eat more—of the right types of food.
Address your nutrition as you would your training.
Tip:
Meal planning is a practical way to prepare and organize your skinny to muscular diet. Knowing what and when you’ll be eating keeps you in control of your intake—and reduces the risk of making wrong food choices.
Here’s what you need to know:
Calculate Your Calories
The number of calories you’ll need for weight gain will depend on your age, your height, and your activity levels.
Estimated calorie intake ranges from 2400-3200 for adult men. For example, if you’re a moderately active 24-year-old man standing at 5-foot-10, you’ll need around 2800 calories to maintain your weight.
Raising your intake might be tough at first—but if you build it up gradually and consistently, your stomach will adapt. Aim to eat 10-15% more every day until you’ve reached your caloric goal.
Tip:
Keep track of what you eat. Designate a day for “weigh-in,” and keep to the same time (morning is usually best). If your results are positive, keep eating the same amount—if not, up your calorie intake.
Macronutrients
Once you determine your daily caloric intake goal, you will need to know how to convert that number to grams for each macronutrient.
I would suggest 35-40% of your macros come from protein, 35-40% from carbs, and about 25-30% from healthy fats.
Use the following calculator to help you partition your macros.
Carbohydrates:
Carbs are the prime source of energy for our bodies. Loading up on this food group is crucial for any exercise—but you’re going to need more fuel for intense workouts such as lifting weights.
The type of carbohydrates you eat is also essential for healthy muscular gain—low GI carbs don’t lead to a spike in blood sugar. Therefore, it’s a more suitable choice for keeping your glucose levels steady.
Here are some examples of healthy carbs you should eat and others you should avoid:
- Good Carbs
- Pasta.
- Brown rice.
- Whole-grain bread.
- Steel-cut oats.
- Beans.
- Most fruits and vegetables.
- Bad Carbs
- Crackers.
- Bagels.
- Croissants.
- Donuts.
- White bread.
- Candy.
Protein:
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is a minimum of 0.36 grams of protein for every pound of body weight.
For example, if you’re a moderately active 24-year-old skinny man at 5 feet 10 inches in height and currently weighing 140 pounds, you’ll need a minimum of 51 grams.
However, that’s to meet your basic nutritional needs. The general rule of thumb is to increase it by at least 1-gram per pound of body weight to gain muscle.
While carbs will make up the majority of your daily calorie intake, it’s protein that will primarily determine how effectively you go from skinny to muscular. You need to eat more protein than your muscles breakdown during exercise.
Protein from animal origins contain higher concentrations per gram and all of the essential amino acids. Conversely, not all plant-based sources are complete—lacking in one or more aminos, and protein content is typically lower.
Some of the best sources of protein include:
- Good Protein Sources
- Lean meats.
- Chicken.
- Fish.
- Eggs.
- Dairy products.
- Lentils and chickpeas.
- Soy-based products.
- Protein supplements.
Fats:
People tend to associate the fats in food with getting fat. They’re not necessarily wrong—it just depends on the type.
Unsaturated fats are an essential part of any healthy diet—they provide you with energy and help regulate your hormones.
One gram of fat contains twice the amount of calories as carbs and protein, so don’t increase it by too much.
Here are some examples of healthy fats you should consume and trans fats and saturated fats can lead to health issues and are best to avoid:
- Healthy Fats
- Fish (salmon, mackerel).
- Avocados.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Olive oil.
- Canola oil.
- Sunflower oil.
- Trans and Sat. Fats
- Processed meats.
- Palm oil.
- Margarine.
- Snack foods (potato chips, cookies).
- Fast food (pizza, hamburgers).
- Pastries.
Meal Plan Example
I’ve formulated a meal plan to help you stick to the above guide and give you an overall idea of what foods you can combine to go from skinny to muscular.
This food database is a practical resource if you want to keep tabs on the nutritional value of the foods you eat.
For reference, this meal plan is based on a 5-foot-10 guy, weighing 140 pounds, who needs to increase his caloric intake to 3300 calories per day to gain muscle.
Meal 1
Three eggs (scrambled)
Yogurt - 1 cup
Whole-grain bread with peanut butter - 2 slices
Meal 2
Mass gainer powder - 1 scoop
Whole Milk - 1 cup
Meal 3
Brown rice - 2 cups
Chicken breast - 8 ounces
Leafy green vegetables (steamed) - 1 cup
Meal 4
Protein powder - 2 scoops
Milk - 2 cups
Banana - 1 piece
Meal 5
Beef - 4-6 ounces
Mixed roast vegetables - 2 cups
One large potato
Tip:
Aim to eat most of your daily protein post-workout. Consuming protein after exercise is proven to aid muscle recovery and growth more effectively.
Skinny to Muscular Workout Plan
When training to go from skinny to muscular, resistance workouts—particularly with heavy weights—are effective. Experts declare that strength training can induce muscle hypertrophy (growth) at an impressive rate.
I’ve listed below a few important skinny to muscular training tips.
- Compound-centric workout, like push, push, and legs routine—avoid excessive isolation exercises (single muscles) and focus on moves that combine multiple muscle groups. This promotes the ultimate mass gains throughout your body. Deadlifts, bench press, squats, dips, and rows are all compound exercises to factor into your workout.
- Train for quality, not quantity—it’s crucial to master the form of each exercise. Incorrectly executing the move means you won’t receive the full benefits. What’s more, you could injure yourself in the process.
- Progressively overload—don’t get comfortable with your weights. If it feels too easy, add heavier plates. Always target the next level, so that your muscles are being worked to their full potential.
- Rest days are essential—overtraining can inhibit the process of muscle repair and regrowth. Dedicate one to two days of the week to giving your body a break.
How to Complete the Workout
- Aim to perform each workout at least once per week—preferably with a rest day in between.
- Add a 10-minute cardio warm-up and cool down to your session and make sure you stretch your muscles properly.
- Complete all sets for the individual exercise before moving on to the next.
- If you’re struggling to hit the rep count, drop some weight. Conversely, if you find it too easy—increase your plates.
Day 1 (low intensity)
Exercise
sets
reps
Rest
Deadlift
4
6
3 mins
Barbell squats
4
6
3 mins
Dumbbell lunges
4
6
3 mins
Pull-ups
4
failure
3 mins
Day 2 (Mideum Intensity)
Exercise
sets
reps
Rest
Stiff-Legged Deadlift
4
6
3 - 5 mins
Bench press
4
10 - 6
3 mins
Bent-Over Barbell Row
4
10 - 6
3 mins
Leg Presses
4
8 - 6
3 mins
Bicep Barbell Curls
4
10 - 6
3 mins
Conclude with Two Abs exercises of your choice.
Day 3 (high intensity)
Exercise
sets
reps
Rest
Overhead Shoulder Press
4
6
3 mins
Deadlift
4
4
3 -5 mins
Barbell squats
4
4
3 - 5 mins
Dips
4
Failure
3 mins
Tricep skull crusher
4
10 - 6
3 mins
No Abs.
Skinny to Muscular Supplements
Supplements are an excellent way to assist your diet for optimal muscle growth.
Creatine
Creatine is produced naturally in your body—it’s function is to provide energy for the muscles—improving your training performance.
Studies show that taking creatine as a dietary supplement can increase the endogenous content in your muscles by up to 40%. Strength gains are also a benefit, which in turn can help increase muscle mass.
It’s one of the most extensively tested supplements. However, with a side effect of water retention, your “true” results could be distorted.
Whey Protein
A byproduct of cheese making, whey contains all the essential amino acids—an excellent source of protein.
With its pro-anabolic traits, whey protein boosts mass growth—enhancing the post-workout recovery process—essential for any skinny to muscular plan.
Adverse reactions include digestive discomfort—cramps, nausea. Furthermore, those who suffer from lactose intolerance should consume whey products with caution.
Weight Gainers
Weight or mass gainers are supplements with high-caloric content—some contain over 1000 calories per serving.
If you find a skinny to muscular diet challenging through foods alone, these can be a convenient way to assist weight gain.
They’re typically carb-laden, but most will also contain a generous amount of protein.
However, research shows that gainer supplements may not be so effective for increasing lean muscle mass in weightlifters.
3 Common Mistakes Skinny Guys Make

1
Not Drinking Enough Water
Dehydration can impair blood flow to the muscles, which could affect your performance.
When you feel thirsty, you’re already dehydrated—make sure to drink an adequate amount of water consistently throughout the day.
2
Skipping Leg Day
Most of us associate massive pecs and biceps with a muscular physique—this isn’t necessarily wrong, just don’t forget about the lower body.
Aim to exercise every major muscle group at least twice a week—it’s good for overall health. Besides, it’ll look pretty weird if you’re balancing a huge upper body on a set of skinny legs.
3
Having Unrealistic Expectations
Going from skinny to muscular is a gradual process that takes time and dedication. You won’t see significant changes in the first couple of weeks—don’t let this demotivate you.
3 Important Tips for Skinny Women
If you thought women had to follow an entirely different game plan, you’d be mistaken. This guide also applies to the skinny sorority—it’s merely a case of a few female-friendly adjustments.
1
Up Your Intake
Buck the trend and watch what you don’t eat. Just like the skinny guys, if you want to build muscle, you need to start adding more calories to your daily quota. The only variation is the final figures won’t be as high as your male counterparts.
2
Hit the Man-Sized Weights
Ditch the dainty dumbbells and bench press alongside the big boys.
To build muscle, pumping heavy iron will fast forward the whole damage—repair—regrow process. Furthermore, contrary to belief, lifting large weights will give you curve appeal—not transform you into Hercules.
3
Supplements Are Not Sex-Specific
With the exception of a few, ergogenic aids are not gender-based. For example, the loading and maintenance phase of creatine supplementation follows the same rules—whether you are a male or female.
The Takeaway
To obtain the ultimate muscular physique—you need to eat more and lift weights. What’s more, food will become your friend—and intensive exercises will give you the results you want.
The key is sticking to it—don’t expect gains by only lifting once a week or gulping down protein shakes now and then.
Consider the above guide your go-to for a complete transformation from skinny to muscular.